Regulation and Licensing: Who Oversees Casinos and What Rules They Must Follow - Security, Fairness, and Regulation: How Casinos Keep Games Legit - What Is a Casino and How Does It Work? A Beginner’s Guide

Casino rules decide if you get fair odds, real payouts, and safe play. Regulation and licensing set those rules. They tell casinos what they can offer, how they must test games, how they must handle your money, and how they must protect your data.
This section sits inside our larger guide, Security, Fairness, and Regulation: How Casinos Keep Games Legit - What Is a Casino and How Does It Work? A Beginner’s Guide.
You will learn who regulates casinos, what a license covers, and which checks matter most. You will also learn the core rules casinos follow on game fairness, anti money laundering, player protection, and dispute handling. You will leave knowing what to look for before you play or deposit.
Casinos run on rules. Regulators set those rules and enforce them. Without oversight, you risk unfair games, weak security, and slow or denied payouts.
This section is part of the larger guide, Security, Fairness, and Regulation: How Casinos Keep Games Legit - What Is a Casino and How Does It Work? A Beginner’s Guide.
You will learn who licenses casinos, what a license covers, and what operators must prove to keep it. You will see the core rules that protect you, game testing and RNG checks, anti-money laundering controls, age and identity checks, payout and advertising rules, and complaint paths. You will also learn how to verify a license and spot red flags fast.
What Is a Casino and How Does It Work? (Beginner Overview)
What a Casino Is
A casino is a house-banked gambling venue or online platform. You place bets on games the operator runs. The casino pays winners from its bankroll and keeps losses as revenue.
Some products run on a different model. Poker rooms and some betting exchanges do not play against you. They charge a fee to host the action.
How Casinos Make Money
Casinos make money through math, volume, and pricing. Your results can vary short term. The long term expectation favors the operator.
- House edge, the built-in advantage in most casino games. It sets your expected loss per bet over time.
- Hold percentage, the share of total wagers the casino keeps after paying wins. It varies by game and player behavior.
- Rake, a fee taken from poker pots or paid as timed seat charges.
- Vigorish, the built-in margin on many sports bets, often expressed through odds pricing.
- Fees, such as payment processing, currency conversion, and some withdrawal charges, depending on the operator and method.
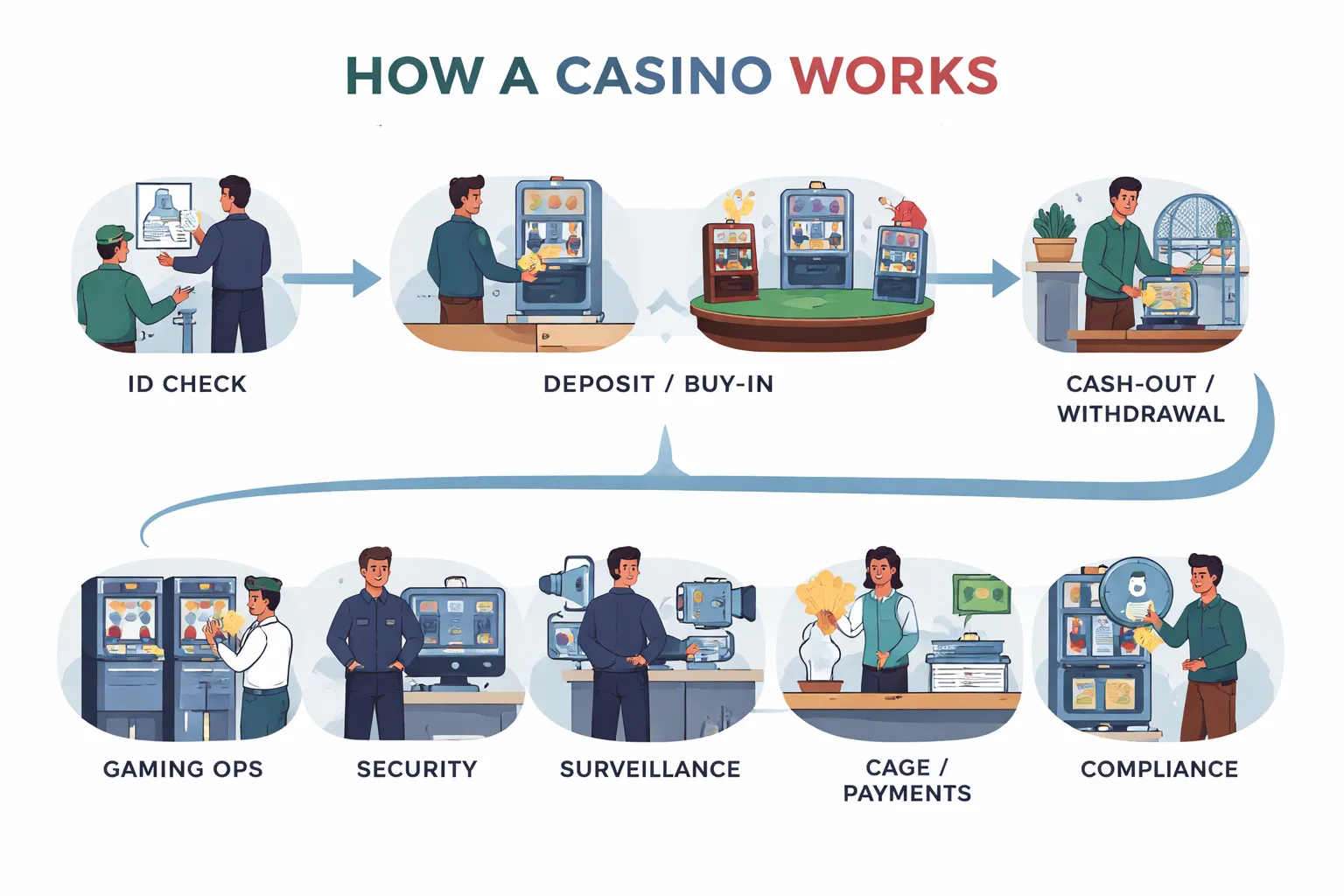
Core Casino Departments You Will Run Into
- Gaming operations, sets game rules, limits, payouts, and handles day-to-day floor or lobby management.
- Security, manages incidents, access control, and on-site safety in land-based casinos.
- Surveillance, monitors games, cash handling, and disputes. Online equivalents rely on logs, fraud tools, and play tracking.
- Cage and payments, handles cash, chips, deposits, withdrawals, and transaction records.
- Compliance, runs AML checks, responsible gambling controls, and licensing reporting.
How a Typical Player Journey Works
Regulated casinos follow a set flow. The exact steps depend on local law, payment method, and your risk profile.
- Account setup and ID checks, you provide personal details. The casino verifies identity and age. Some checks happen before you deposit, others before your first withdrawal.
- Buy-in or deposit, you exchange cash for chips, or fund your online balance. The casino logs the transaction.
- Gameplay, the system records bets, outcomes, and session history. Table games rely on dealer procedures and pit oversight. Online games rely on software logs and RNG results.
- Cash-out or withdrawal, you redeem chips or request a payout. The casino may ask for documents, confirm payment ownership, and run AML screening before approval.
- Disputes and support, you contact support first. If you play in a regulated market, you may have access to an independent complaints process.
Common Game Types Explained
- Slots, you bet per spin. Outcomes come from a random number generator in online slots, or certified internal logic in electronic machines. Payouts follow a defined paytable and RTP setting.
- Table games, like blackjack, roulette, and baccarat. Rules and side bets change the house edge. Limits control variance and exposure for you and the casino.
- Poker, you play other players. The casino earns from rake or seat time. Integrity controls focus on collusion, bots online, and chip dumping.
- Sports betting, where legal. You bet on events at posted odds. The operator manages risk through pricing, limits, and balancing its book, plus hedging in some markets.
| Product | Who you play against | How the casino gets paid |
|---|---|---|
| Slots | The house | House edge, hold percentage |
| Table games | The house | House edge, side bet edge |
| Poker | Other players | Rake, seat fees |
| Sports betting | The house | Odds margin, limits, risk management |
What Is a Casino and How Does It Work? (Beginner Basics)
What a casino is, land based vs online
A casino is a regulated gambling business. It offers games where the house sets the rules, takes a built in advantage, and pays winners from its bankroll.
- Land based casinos run games on a physical floor. You use cash, chips, tickets, or a player card. Staff handle dealing, payouts, and security in person.
- Online casinos run games on a website or app. You use digital deposits and withdrawals. Games run on software, random number generators, and remote live dealer studios.
Both types must follow license rules on fairness, identity checks, anti money laundering, and player protection. The methods differ, the controls stay the same.
How casinos make money, house edge and hold
Casinos price every game for profit. They do it with the house edge.
- House edge is the average share of each bet the casino expects to keep over time. Example, a 5% edge means the long run cost is about $5 per $100 wagered.
- Hold percentage is what the casino actually keeps over a period. Hold moves because players can win big in the short term.
Do not confuse edge with short term results. You can win today in a negative expectation game. The math catches up across many bets.
Volatility vs edge, why swings happen
Volatility measures how much results swing. It does not tell you the long run cost.
- Low volatility games pay smaller wins more often, you see steadier bankroll changes.
- High volatility games pay less often but can pay large jackpots, you see long losing runs and sudden spikes.
A game can have a low edge and high volatility, or a high edge and low volatility. Check both before you set a budget.
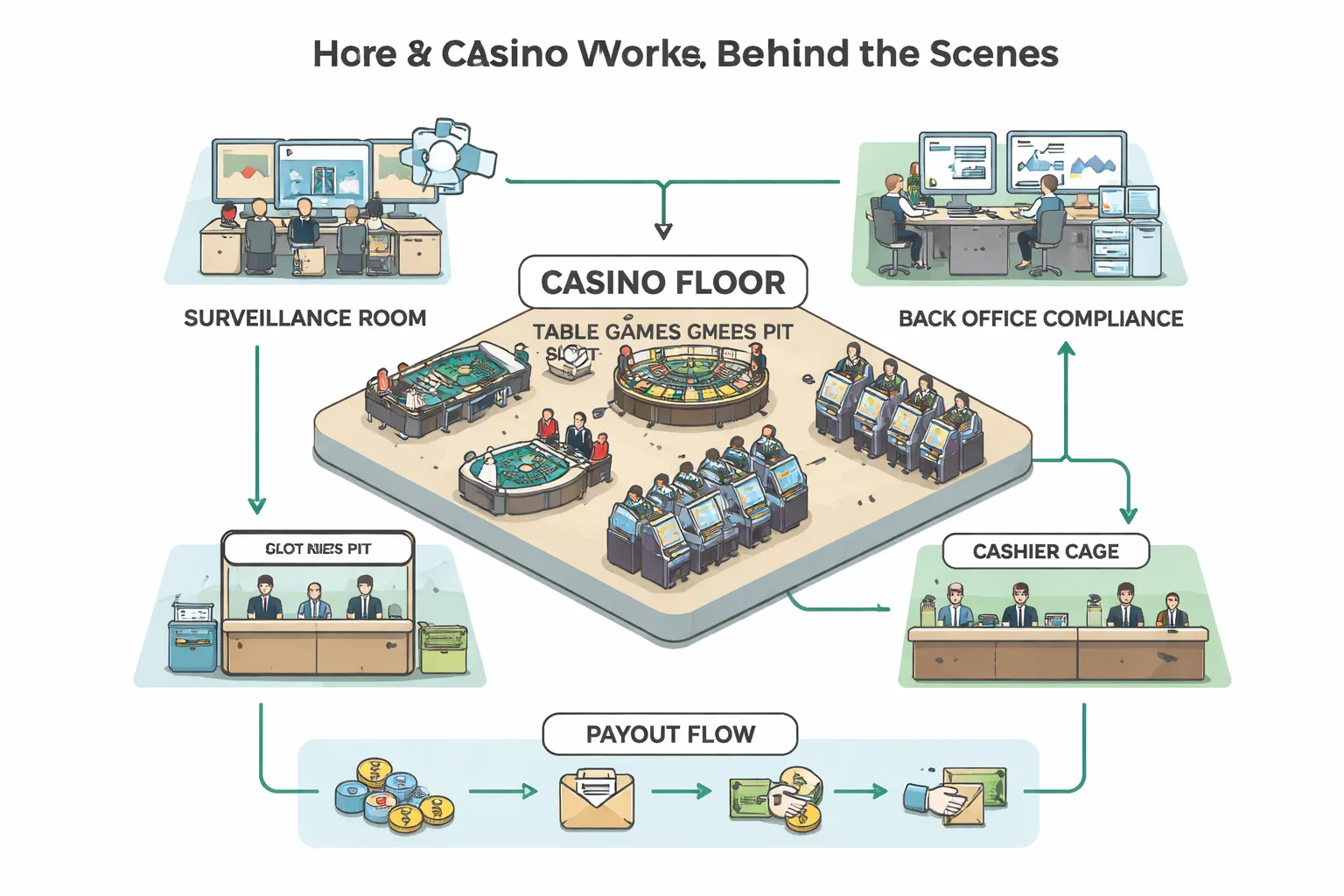
What happens behind the scenes
A casino runs like a cash handling and risk business. Games sit on the surface. Controls sit underneath.
- Cage, the cashier hub. It handles cash, chip redemptions, jackpots, wires, and large transactions. It also logs reports tied to anti money laundering rules.
- Chips and chip inventory. The casino tracks chips by denomination and table. It uses fill and credit slips so every movement matches a record.
- Credit markers. In many land based casinos, approved players can borrow funds. The casino issues a marker, then collects it like a short term loan.
- Payouts. Slots may pay from a machine and require a hand pay over set thresholds. Table games pay from the table bankroll, then the floor reconciles results.
- Bankroll management. The casino sets table limits, reserves, and procedures so it can cover wins even on unusual nights.
Key roles that keep games controlled
- Dealers run table games, enforce betting rules, and pay according to posted procedures.
- Pit bosses and floor supervisors watch tables, approve exceptions, and handle disputes fast.
- Surveillance monitors cameras, reviews play, and investigates cheating, theft, and collusion.
- Compliance officers oversee identity checks, anti money laundering controls, record keeping, and responsible gambling processes.
Common game categories you will see
- Table games, blackjack, roulette, baccarat, craps, and other dealer run games. Rules and limits vary by property and jurisdiction.
- Slots, reel games and video slots. Results come from software, not physical reels, even when the cabinet looks mechanical.
- Poker rooms, player versus player. The casino earns by taking a rake per pot or charging time fees, not by betting against you.
- Sports betting, where legal. You bet on event outcomes. The operator earns through pricing and risk management, not a fixed house edge per bet.
Regulation and Licensing: Who Oversees Casinos and What Rules They Must Follow
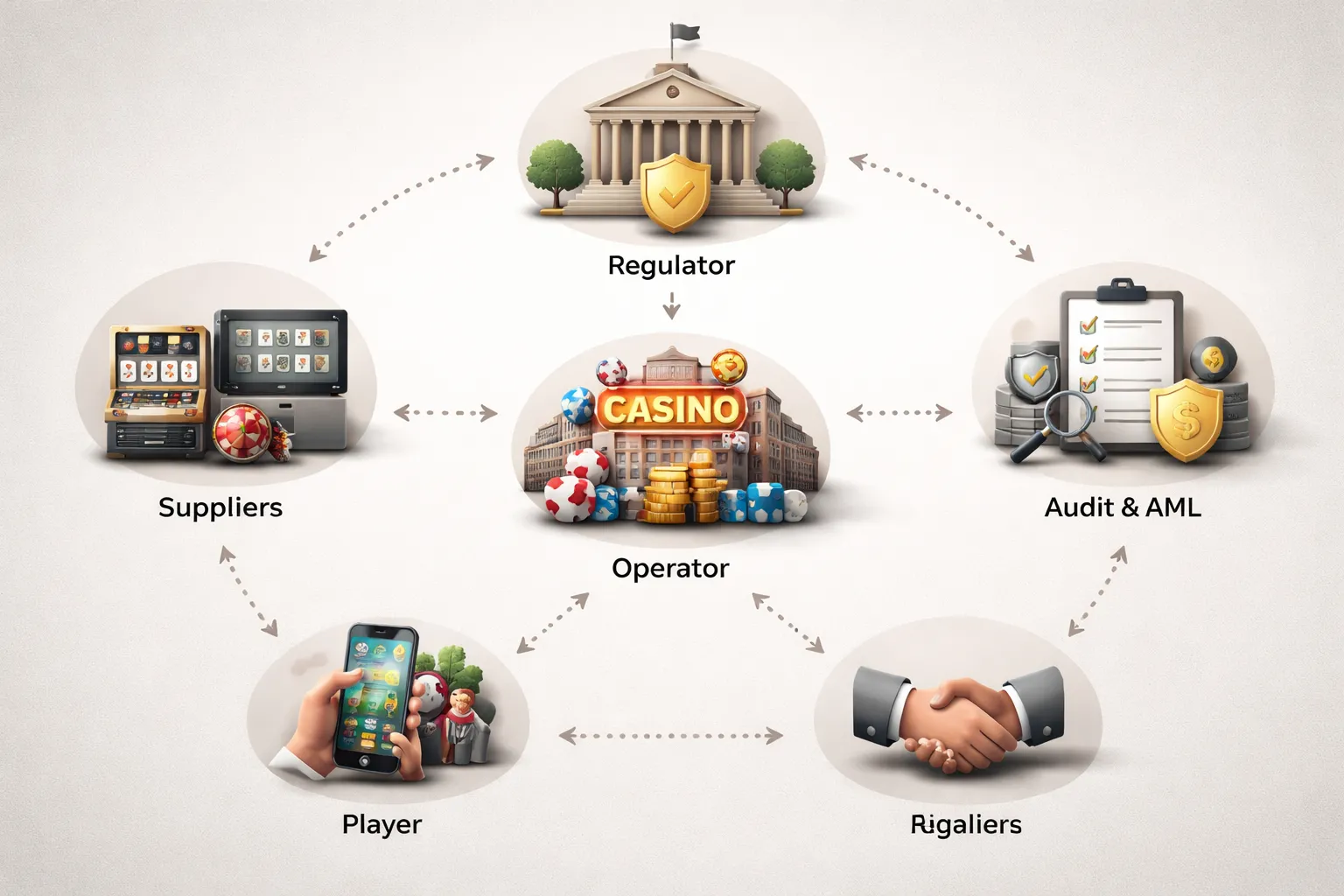
Who regulates casinos
Casinos run under government oversight. The main regulator is usually a gaming commission or gambling authority. It writes rules, issues licenses, audits results, and can fine or shut operators down.
Regulators work with law enforcement and financial watchdogs. You see this in anti money laundering checks, fraud investigations, and illegal gambling enforcement. Tax agencies also play a role because casinos report revenue and pay gaming taxes.
How licensing works
Licensing starts with an application. The operator submits ownership details, funding sources, business plans, internal controls, and key staff names.
- Suitability checks: Regulators test whether owners and executives meet “fit and proper” standards. You can expect checks on criminal history, civil judgments, and past regulatory actions.
- Background investigations: Regulators verify identity, funds, and beneficial ownership. They review bank records, corporate structure, and major contracts.
- Control approval: The casino must document how it handles cash, payouts, surveillance, disputes, and game rules.
- Ongoing renewals: Licenses do not run forever. Regulators require renewals, annual reporting, and updates when ownership or key people change.
If the regulator finds hidden ownership, weak controls, or bad funds, you often see denial, suspension, or heavy conditions.
Core compliance areas casinos must follow
- AML and KYC: Casinos must know who you are in many situations and track risky activity. They set thresholds for ID checks, monitor large cash movement, and file required reports. You may need to show ID to cash out, withdraw online, or move big amounts.
- Responsible gambling: Rules cover self exclusion, age checks, deposit limits, and help resources. Some markets require cooling off periods and safer gambling messages in the lobby and online.
- Advertising rules: Regulators restrict targeting minors, misleading “risk free” claims, and unclear bonus terms. You should see key terms shown with the offer, including wagering requirements where they apply.
- Game integrity and fairness: Slots and online games must use certified random number generators. Table games must follow approved rules. Regulators test payout settings, inspect procedures, and review complaints.
- Data and privacy for online casinos: Online operators must protect your account data and payment details. Many jurisdictions require encryption, access controls, breach reporting, and limits on how data gets shared with third parties.
Operator licenses vs supplier and manufacturer licenses
An operator license lets a company offer gambling to you. It covers the brand, the website or property, payment handling, customer support, and compliance systems.
A supplier or manufacturer license covers the companies that build the parts. That includes slot machines, game software, RNGs, live dealer studios, and sometimes payment or platform providers. Regulators license suppliers to stop bad actors from entering the market through the back door.
Jurisdiction matters
Rules change by country, state, and province. Some places allow online casinos, others ban them. Some allow sports betting but restrict casino games. Tax rates, bonus limits, ID rules, and self exclusion systems also vary.
This affects you in practical ways.
- You may get different games and promos depending on your location.
- Your verification steps can be stricter in one market than another.
- Your dispute options depend on the regulator. A strong regulator gives you a clear complaint process and an escalation path.
- Your protections vary. Look for a named license, a license number, and a regulator you can contact.
Security and Surveillance: How Casinos Prevent Cheating, Theft, and Fraud
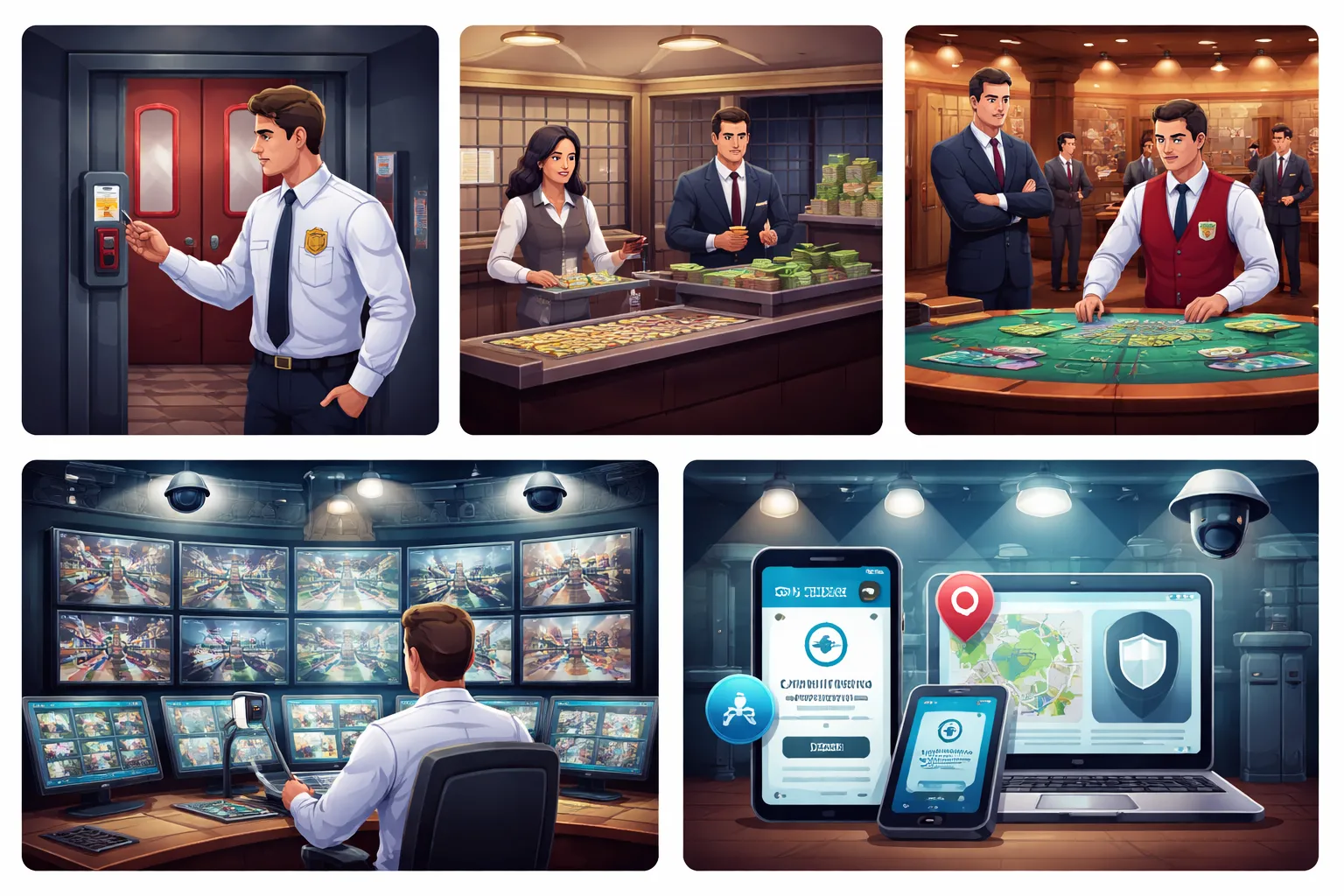

Physical security basics
Casinos treat the floor like a controlled site. They manage who enters, where staff can go, and how money and chips move.
- Access control: Staff use badges, locked doors, and restricted routes to reach the cage, count room, surveillance, and vault. Security logs entries and exits.
- Chip and asset protection: Casinos store high value chips, cash, and tickets in secured areas. They track inventory by shift, table, and denomination.
- Table procedures: Dealers follow set steps for shuffles, cuts, payouts, fills, and credits. Supervisors watch for deviations. Small process breaks can signal a bigger problem.
Surveillance operations
Surveillance gives the casino a record. It supports real-time detection and post-incident proof.
- Camera coverage: Casinos place cameras on table games, the cage, entrances, and high risk corridors. They prioritize hands, chips, and cash movement.
- Monitoring practices: Teams watch live feeds, review alerts, and pull clips when staff report unusual play, disputes, or suspected cheating.
- Evidence retention: Casinos keep footage and transaction logs for a defined period, often longer for incidents. If you file a dispute, time matters. Report issues fast so footage stays available.
Common threats casinos look for
Most scams target the same weak points. Casinos train staff to spot patterns, not personalities.
- Card marking: Players alter cards with scratches, bends, ink, or edge work. Staff watch for unusual card handling and repeated requests to change decks.
- Collusion: Two or more players share information in poker or coordinate bets in table games. Casinos use seating controls, play reviews, and betting pattern checks.
- Device cheating: Hidden earpieces, phones, or analyzers help track cards or influence outcomes. Many properties ban phones at certain tables and enforce strict hand visibility rules.
- Slot tampering: Attempts include ticket fraud, machine access, button overlays, or hardware interference. Slots log errors and door opens, and tech teams reconcile events with footage.
- Counterfeit chips: Fakes try to enter circulation at busy times. Real chips use embedded security features and designs that cameras and staff can verify.
- Cage fraud: Risks include forged IDs, altered slips, short pays, and internal theft. Casinos split duties, require approvals, and reconcile drawers to detect gaps fast.
Online security controls
Online casinos focus on account integrity, payments, and location rules. These systems protect you and protect the license.
- Account protection: Strong passwords, two-factor authentication, and login alerts reduce takeover risk. If you reuse passwords, you raise your odds of loss.
- Payment security: Operators monitor deposits, chargebacks, and unusual withdrawal behavior. They use risk scoring and step-up checks before payouts.
- Geolocation: Licensed sites must confirm you play from an allowed area. They use GPS, Wi‑Fi signals, and IP checks, and they block play when signals conflict.
- Device fingerprinting: Platforms track device traits to detect multi-accounting, bonus abuse, and repeated fraud patterns.
Incident response and regulator involvement
Casinos follow a playbook when something goes wrong. The goal is to preserve evidence and meet legal duties.
- Immediate action: Staff pause play, secure chips or cash, and call a supervisor. Surveillance flags and saves related footage.
- Investigation: The casino pulls table logs, slot event logs, player tracking data, cage records, and footage. They interview staff and document a timeline.
- Reporting obligations: Many jurisdictions require reports for suspected cheating, major theft, money laundering indicators, or system failures that affect game integrity.
- When regulators get involved: Regulators may request footage, audit trails, and internal reports. They can order corrective actions, issue fines, or suspend operations.
Fairness and Game Integrity: How Casinos Keep Games Legit

How Casinos Ensure Randomness
You rely on randomness. Casinos prove it in different ways for machines, online games, and live tables.
Slots and online casino games use an RNG. RNG means Random Number Generator. It produces numbers fast, even when nobody plays. When you press spin or deal, the game takes the next result from that stream and maps it to symbols, cards, or outcomes.
Live card games use shuffles and cuts. Dealers shuffle by hand or with approved shuffling machines. Many tables also use a cut card. In some rooms, you can ask for a new deck setup and a fresh shuffle.
Dice games control the physical roll. Casinos use standard dice procedures to reduce bias and manipulation.
Game Certification and Testing Labs
You do not have to trust the casino’s word. Regulators often require independent testing before a game goes live and after major changes.
- RNG testing. Labs review RNG design, seeding, and output behavior. They test for predictable patterns and repeatable sequences.
- Game math verification. Labs confirm paytables, hit frequency, bonus behavior, and the theoretical return match the submitted game specs.
- Software integrity. Labs check code signing, version control, and checksum methods. They confirm the deployed build matches the certified build.
- Ongoing compliance checks. Some jurisdictions require periodic audits, field inspections, and reporting when a game version changes.
RTP and Payout Disclosures, What They Mean and What They Don’t
RTP stands for Return to Player. It is a long-run average. If a slot lists 96% RTP, it means the game is designed to return about 96 units for every 100 units wagered over a very large number of spins.
- RTP does not predict your session. You can win or lose a lot in the short term.
- RTP does not guarantee equal results for all players. Outcomes vary by variance and sample size.
- RTP may vary by version or jurisdiction. Some games allow different RTP settings. Regulators may restrict which settings a casino can offer and how they disclose them.
Payback and jackpot rules also have limits. Progressive jackpots follow defined contribution rates and trigger conditions. The casino and the supplier must log meters, hits, and resets.
Table Game Controls
Table games rely on procedures. Casinos train staff to follow them the same way every time.
- Table audits. Supervisors and count teams reconcile chips, fills, and credits. They compare table inventory and drop boxes against reported numbers.
- Card handling. Staff seal, log, and store decks. Dealers wash and shuffle in view. They use a cut card. They replace damaged cards fast.
- Shufflers and shoes. If the casino uses shufflers, they use approved models and track maintenance. They inspect shoes and discard racks.
- Dice controls. Stick staff present dice for inspection. They swap dice on schedule or when damage shows. They enforce clean throws and wall contact rules.
- Dealer training and rotation. Dealers learn set procedures for payouts, hand signals, and game calls. Casinos rotate dealers and supervisors to reduce collusion risk.
Player Dispute Handling
If you challenge a result or payout, the casino follows a defined path.
- Step 1, stop and call a supervisor. Ask for a floor manager before the next hand or spin if possible.
- Step 2, review the evidence. Staff check table procedures, game logs, jackpot meters, and system records. For live games, they pull camera footage.
- Step 3, document the outcome. The casino records your claim, the time, the machine or table ID, and the final decision.
- Step 4, escalate if needed. If you still disagree, ask for the regulator complaint process. Many regulators accept player complaints and can request logs and footage.
Act fast. Many properties keep detailed footage, but retention windows vary. Your best leverage is clear details, time, location, and what you saw.
Responsible Gambling and Consumer Protection Rules You’ll See in Regulated Casinos
Self-exclusion and cooling-off programs
Regulated casinos must give you tools to block your access. These programs exist in land-based venues and online.
- Cooling-off: A short break. You choose a period, often 24 hours to several weeks. You cannot gamble during that time.
- Self-exclusion: A longer ban, often months to years. Some jurisdictions allow permanent exclusion.
- Scope: In strong systems, exclusion applies across many venues and sites in the same jurisdiction, not just one brand.
- Enforcement: Staff must refuse entry, void access, and stop marketing to excluded players. Online accounts must lock and prevent deposits and play.
- Reinstatement: Many regulators require a minimum period, a formal request, and a waiting period before reactivation.
Keep a copy of your exclusion confirmation. Save emails, screenshots, and dates. If a casino lets you play while excluded, you have clear grounds for a complaint.
Deposit, loss, and time limits, plus reality checks (online)
Online regulated casinos usually must offer limit controls inside your account. You set them. The site must enforce them.
- Deposit limits: Cap how much you can add per day, week, or month.
- Loss limits: Cap your net loss over a period. Rules differ by regulator, so read the definition in the help pages.
- Wager limits: Cap the total amount you stake.
- Time limits: Set session length or total time per day.
- Reality checks: Pop-ups that show time played, spend, and wins or losses. They force a pause and confirmation.
- Limit changes: Tightening a limit should apply fast. Raising a limit often triggers a delay, such as 24 hours or more, to slow impulse decisions.
Use limits before you start playing. Set them when you feel calm. Treat them as hard rules, not suggestions.
Age verification and identity checks
Regulated casinos must keep minors out and confirm who you are. You will see checks at the door, online, or both.
- Land-based ID checks: Security or floor staff can ask for ID at entry, at the cage, or when you hit a payout threshold.
- Online KYC: You may need to upload an ID, proof of address, and sometimes a payment method check.
- Source of funds checks: For higher activity, some operators must ask where your money comes from. This links to anti-money laundering rules.
- Account integrity: One person, one account. Casinos can restrict or close accounts if they detect duplicates or false details.
If you want fast withdrawals, verify early. Do it before you deposit large amounts. Keep your documents current and readable.
Marketing restrictions and bonus terms transparency
Regulators control how casinos advertise and how they present promotions. You should see clearer terms and fewer traps in well-regulated markets.
- Bonus terms must be readable: Wagering requirements, game contribution, max bet, expiry dates, and withdrawal conditions should appear in the offer and the full terms.
- Opt-out rules: You should be able to stop marketing emails and texts. Self-excluded players should not receive promos.
- Targeting limits: Many regulators ban ads aimed at minors and restrict content that glamorizes risky play.
- Affiliate control: In regulated markets, operators often remain responsible for affiliate claims. Misleading ads can trigger enforcement.
Before you take a bonus, check five items. Wagering multiple, max bet while wagering, excluded games, withdrawal cap, and time limit.
Where to get help
Regulated casinos must post responsible gambling info and direct links to help. You can also go straight to the regulator.
- Casino tools: Account limits, time-outs, self-exclusion, transaction history, and a clear complaints route.
- Regulator resources: License lookup, rules for player disputes, and complaint forms. Many regulators can request logs and game records.
- Support organizations: National helplines, counseling services, and chat support. Look for independent groups, not casino-run programs.
- Payment blocks: Some banks and payment apps offer gambling blocks. Use them if limits alone do not hold.
If you feel out of control, stop play, block access, and contact a support service the same day. Save your account history and any chats with support.
How to Tell if a Casino Is Legit: A Beginner Checklist
Verifying a License: Where to Look and How to Confirm It
Start with the footer. Legit casinos show a license number, the regulator name, and the legal operator name. If you only see a logo with no number, treat it as unverified.
- Match names. The operator name in the footer must match the name in the Terms and Conditions and the payment recipient name.
- Check the regulator site. Use the regulator’s official license search. Confirm the status shows active, and the domain you use appears on the license record.
- Confirm the address. A real operator lists a registered address and company number. If you cannot validate the company in a public registry, stop.
- Verify the game suppliers. Reputable casinos list game providers. Cross-check on the provider’s site if the operator appears as an approved partner.
Red Flags That Signal a Risky Casino
- Unclear ownership. No legal entity name, no address, or only a brand name.
- Missing or thin Terms. No clear rules on withdrawals, bonuses, verification, or account closure.
- Unverifiable audits. Claims like “RNG certified” with no lab name, no report date, and no certificate link you can confirm.
- Payout complaints with a pattern. Reports of delayed cashouts, repeated extra document requests, or “confiscated winnings” tied to vague bonus rules.
- Rogue jurisdictions. A license from a place with weak enforcement, no public register, or no player complaint path. If you cannot verify the license on an official site, treat it as no license.
- Bad security signals. No HTTPS, broken pages in cashier or support, or support that refuses to answer basic licensing questions.
Safe Payment Practices and Responsible Play Steps
- Use payments with dispute options. Cards and major wallets can give you clearer records than wire transfers or crypto.
- Separate your bankroll. Use a dedicated account or wallet. Do not mix gambling funds with rent and bills.
- Start small. Make a low deposit and a small withdrawal early. Test speed and document requests before you scale.
- Read bonus terms before you opt in. Check wagering rules, max cashout, excluded games, and withdrawal limits.
- Set limits on day one. Deposit limit, loss limit, time limit. Use self-exclusion if you chase losses.
- Keep records. Save receipts, withdrawal confirmations, and support transcripts. Take screenshots of promo terms.
What to Do if There’s a Dispute
Move in steps. Stay factual. Keep everything in writing.
- Step 1, operator escalation. Contact support with your account ID, transaction IDs, dates, and exact issue. Ask for a case number and the complaints procedure.
- Step 2, formal complaint. Submit a written complaint under their Terms. Include evidence. Set a clear deadline for response.
- Step 3, ADR or mediation. If the casino lists an ADR provider, file there. Provide the full timeline and attachments. Do not send new money while the case stays open.
- Step 4, regulator complaint. File with the licensing authority. Use the regulator’s complaint form and attach your evidence, plus the casino’s replies or lack of reply.
- Step 5, payment dispute. If you used a card or wallet, ask your provider about chargeback or dispute rules. Act fast, many systems have strict time windows.
If the casino blocks you, removes chats, or changes terms mid-case, stop play and export your account history the same day.
Key Takeaways
- In het kort: A licensed casino answers to a regulator; an unlicensed one answers to nobody.
- In het kort: Regulators set rules for game fairness, security, and responsible gambling, then audit and enforce them.
- In het kort: You protect yourself by verifying the license, reading bonus terms, and keeping your own records.
- In het kort: When a dispute starts, stop play and collect evidence the same day.
- In het kort: Escalate in a fixed order, casino support, formal complaint, regulator, then payment dispute if needed.
Check the casino footer for the license number and regulator name. Match it on the regulator’s public register. If the register does not list the operator, treat the site as unregulated.
Fairness controls focus on certified RNGs, tested return-to-player settings, and game logs that allow audits. Security controls focus on identity checks, fraud monitoring, and safe payment handling. Responsible gambling rules require limits, self-exclusion, and clear help access.
For complaints, use a simple file set. Save screenshots, timestamps, transaction IDs, game round IDs, bonus terms, and all chat or email replies. Submit the same pack to the regulator if the casino stalls or refuses to act.
FAQ
Who regulates casinos?
It depends on the casino’s license. Land-based casinos answer to a local gaming commission. Online casinos answer to a national regulator in the country that issued the license. Check the footer and the license page for the authority name and license number.
How can you verify a casino license?
Match the casino name and license number to the regulator’s public register. Confirm the legal entity, website domain, and license status. If the casino lists a license but the register shows no match, treat it as unlicensed.
What rules must licensed casinos follow?
Core rules cover player verification, anti-fraud controls, protected customer funds, game testing, and complaint handling. Many regulators also require responsible gambling tools like deposit limits and self-exclusion. The exact list varies by jurisdiction.
How do casinos prove games are fair?
They use certified random number generators and independent lab testing. Regulators often require test reports and ongoing checks after updates. You should see the testing lab name and certificate details in the casino’s footer or legal pages.
What security checks should you expect?
Expect ID checks, age checks, and payment verification. Casinos also monitor logins, unusual betting, and chargeback risk. Use strong passwords and two-factor login if offered. Avoid sharing accounts or using unknown payment methods.
What is KYC and why does it matter?
KYC means the casino verifies your identity. It helps stop fraud, underage gambling, and money laundering. If you fail KYC, the casino can block withdrawals. Submit clear documents that match your account details and payment method.
How do complaints and disputes work?
Start with the casino’s support team and request a written case number. If you get no resolution, escalate to the regulator or an approved dispute service. Send a single file set with screenshots, timestamps, IDs, bonus terms, and full chat logs.
Can a casino void winnings for bonuses?
Yes, if you break the bonus terms. Common triggers include exceeding max bet, using restricted games, or linked accounts. Save the bonus page and terms before you play. If the terms changed, ask for the version tied to your claim.
What responsible gambling tools should you use?
Set deposit and loss limits before you play. Use session time reminders. Use self-exclusion if you cannot control play. Keep proof of any limit request. For support options, see /where-to-get-help-for-gambling-addiction-your-options-from-free-support-to-treatment-signs-of-gambli.html.
What should you do if a casino delays your withdrawal?
Check KYC status, withdrawal limits, and processing times in the terms. Ask for the exact reason and a timeline in writing. Stop depositing until it clears. If delays exceed the stated timeframe, file a complaint with your evidence pack.
Conclusion
Casino rules are not optional. Regulators set the minimum standards for licensing, game fairness, player funds, KYC, and dispute handling. You protect yourself when you treat those standards as a checklist, not marketing.
- Verify the license on the casino site and match it to the regulator’s public register.
- Read the terms that affect cashouts, KYC, withdrawal limits, processing times, and bonus wagering rules.
- Track your paper trail, save screenshots, emails, chat logs, and transaction IDs.
- Use the right escalation path, support first, then the formal complaints route listed by the regulator, then ADR if offered.
- Set hard limits, deposit, loss, and time. Use self-exclusion if you need it.
Final tip, before you play, test the withdrawal process. Deposit a small amount, complete KYC early, then cash out once. If the casino misses its own stated timeframe, stop depositing and file a complaint with your evidence pack.
-
Security, Fairness, and Regulation: How Casinos Keep Games Legit - What Is a Casino and How Does It Work? A Beginner’s Guide
1 week ago -
Fairness in Casino Games: RNGs, Odds, House Edge, and Return-to-Player (RTP) - Security, Fairness, and Regulation: How Casinos Keep Games Legit - What Is a Casino and How Does It Work? A Beginner’s Guide
1 week ago
-
- Who regulates casinos?
- How can you verify a casino license?
- What rules must licensed casinos follow?
- How do casinos prove games are fair?
- What security checks should you expect?
- What is KYC and why does it matter?
- How do complaints and disputes work?
- Can a casino void winnings for bonuses?
- What responsible gambling tools should you use?
- What should you do if a casino delays your withdrawal?
-
-
- Who regulates casinos?
- How can you verify a casino license?
- What rules must licensed casinos follow?
- How do casinos prove games are fair?
- What security checks should you expect?
- What is KYC and why does it matter?
- How do complaints and disputes work?
- Can a casino void winnings for bonuses?
- What responsible gambling tools should you use?
- What should you do if a casino delays your withdrawal?
-
-
Fairness in Casino Games: RNGs, Odds, House Edge, and Return-to-Player (RTP) - Security, Fairness, and Regulation: How Casinos Keep Games Legit - What Is a Casino and How Does It Work? A Beginner’s Guide
1 week ago -
Security, Fairness, and Regulation: How Casinos Keep Games Legit - What Is a Casino and How Does It Work? A Beginner’s Guide
1 week ago -
What Is a Casino and How Does It Work? A Beginner’s Guide
1 week ago -
How Casinos Make Money: House Edge, RTP, and the Math Behind It
1 week ago -
Casino Terminology Glossary: House Edge, RTP, Variance, and More
1 week ago
-
Security, Fairness, and Regulation: How Casinos Keep Games Legit - What Is a Casino and How Does It Work? A Beginner’s Guide
1 week ago -
RTP Explained: How to Use Return to Player to Choose Slots
1 week ago -
What Is a Casino and How Does It Work? A Beginner’s Guide
1 week ago -
Casino RNG Explained: How Random Number Generators Work
1 week ago -
How to Set a Gambling Budget (and Stick to It)
1 week ago